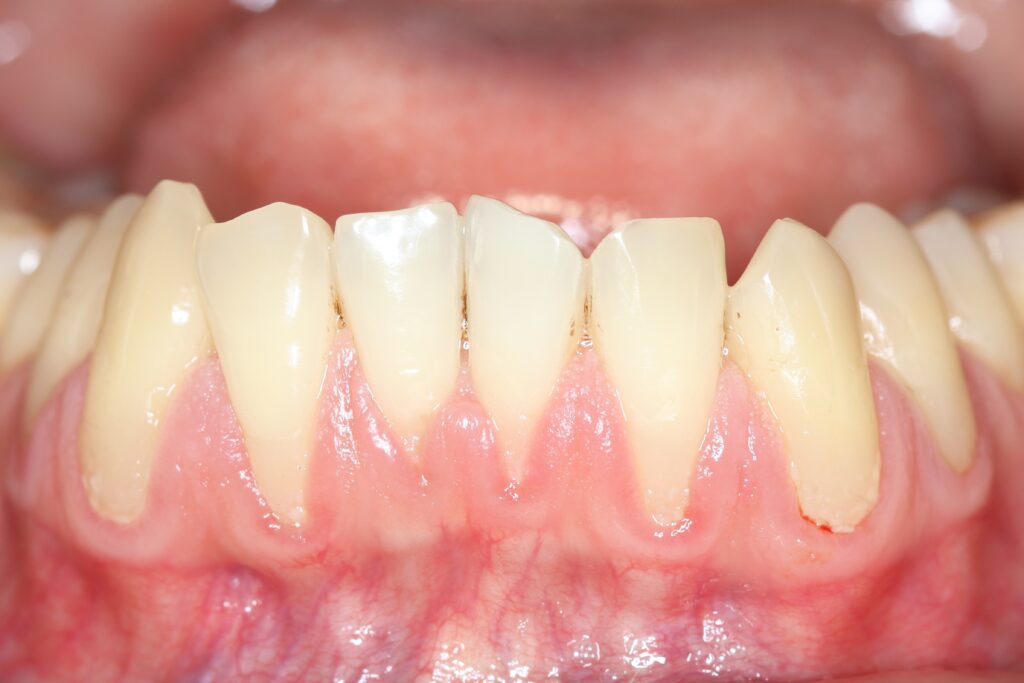
Gum Recession
Gum recession is a condition characterized by the gums gradually pulling away from the tooth, thereby exposing more of the tooth or its root. If left unchecked, it can lead to a myriad of oral health complications. This article aims to illuminate the subject of gum recession, its causes, symptoms, and the intricacies of this dental issue. With this information at your disposal, we will navigate through the various treatment options and preventative measures to combat gum recession. This comprehensive guide will equip you with the knowledge to understand the impact of gum recession on your oral health and how to confidently tackle this dental condition.
What is Gum Recession and its Causes?
Gum recession is a dental condition where the gum tissue surrounding the teeth starts to recede or wear away, resulting in more exposure of the tooth or its root. This process creates gaps or pockets between the teeth and gum line, providing a conducive environment for harmful bacteria to accumulate. If neglected, this can lead to severe damage to the bone structure of the teeth and potentially result in tooth loss.
Several factors can instigate or contribute to gum recession, including:
- Periodontal Diseases: These bacterial gum infections can obliterate gum tissue and the supporting bone that secures your teeth in place. Periodontal disease is the primary culprit behind gum recession.
- Genetics: Certain individuals may have a genetic predisposition to gum recession. Despite maintaining excellent oral health practices, these individuals are more prone to gum recession due to their thin gingival biotype.
- Aggressive Tooth Brushing: Brushing your teeth too vigorously or incorrectly can erode the enamel on your teeth and cause your gums to recede. Using a hard bristle toothbrush is one of the most common causes of gum recession. Be sure to opt for a soft bristle toothbrush when brushing.
- Poor Dental Care: Insufficient brushing, flossing, and rinsing with antibacterial mouthwash can allow plaque to harden into tartar—a substance that can only be removed by professional dental cleaning and can trigger gum recession.
- Tobacco Products: Tobacco users often have sticky plaque on their teeth that is difficult to remove, leading to gum recession.
- Hormonal Changes: Changes in female hormone levels during various life stages, such as puberty, pregnancy, and menopause, can render gums more sensitive and susceptible to gum recession.
- Clenching or Grinding Your Teeth: These habits exert excessive force on the teeth, causing the gums to recede.
- Crooked Teeth or a Misaligned Bite: When teeth don’t align properly, excessive force can be exerted on the gums and bone, leading to gum recession.
Recognizing the causes of gum recession is a critical step towards its prevention and early treatment. If you notice any signs of gum recession, it’s imperative to consult your dentist promptly.
Symptoms of Gum Recession
Gum recession is a prevalent oral health issue, yet its gradual progression can make early detection challenging. Recognizing the initial signs is crucial for timely intervention and professional dental care. Here are several indicators to keep an eye on:
- Lengthening Teeth: An illusion of elongated teeth is a classic sign of gum recession. As gums pull back, more of the tooth surface becomes visible, creating this effect.
- Revealed Tooth Roots: The exposure of tooth roots is a primary symptom of gum recession. This not only affects your smile aesthetically but can also lead to heightened sensitivity.
- Increased Tooth Sensitivity: When gums recede, they expose tooth roots that lack the protective hard enamel. This can result in heightened sensitivity to temperature extremes and various food and drink flavors.
- Inflamed, Red Gums: Redness or swelling in your gums could indicate gum disease, which often accompanies gum recession.
- Bleeding Post Brushing or Flossing: If you notice bleeding after your oral hygiene routine, it could be a sign of gum disease and potential gum recession.
- Loosening Teeth: Advanced gum recession can compromise the supporting tissue and bone structures of the teeth, leading to loose teeth.
- Altered Bite: Changes in how your teeth fit together could be a result of shifting gum tissue, another potential sign of gum recession.
Any alterations in your gums warrant a dental consultation. Early gum recession detection is vital to halt the issue and prevent further gum and bone loss. The sooner the intervention, the more favorable the prognosis.
Gum Recession: Treatments and Prevention
Addressing gum recession involves several key objectives: treating the underlying cause, safeguarding your teeth, halting further tissue loss, and, if necessary, regenerating lost tissue. The severity of the gum recession dictates the approach, ranging from preventive measures to halt progression to more comprehensive treatment options. Emphasizing proper dental care is paramount in preventing gum recession. This section delves into the various strategies for managing gum recession and how to shield yourself from this oral health concern.
Treatment Options for Gum Recession
When it comes to addressing gum recession, the treatment plan is tailored to the individual, taking into account the extent of the condition and its root cause. Here’s a look at some of the most common strategies used to combat gum recession:
- Adopting a Rigorous Oral Hygiene Routine: In the initial stages, enhancing your oral hygiene regimen can often halt the disease’s progression. Regular brushing, flossing, and dental visits can effectively keep gum recession at bay.
- Undergoing Scaling and Root Planing: This deep cleaning procedure involves the removal of plaque and tartar from the tooth and root surfaces beneath the gum line, fostering an environment that promotes gum tissue healing.
- Utilizing Antibiotics: If an active infection is exacerbating gum inflammation, your dentist may recommend a course of topical or systemic antibiotics.
- Considering Gum Graft Surgery: For more advanced cases, a dental surgeon might propose a gum graft. This procedure involves transplanting a small piece of tissue from another part of your mouth, often the palate, to the areas experiencing gum recession, protecting exposed roots and encouraging tissue growth.
- Exploring the Pinhole Surgical Technique (PST): This innovative, minimally invasive method treats gum recession by creating a small entry point in the gum. Specialized tools are then used to loosen and shift the gum tissue over the receding areas.
- Investigating Regenerative Procedures: If recession has resulted in bone loss around your teeth, a regenerative procedure might be suggested to stimulate new bone tissue growth.
Remember, early detection of gum recession simplifies treatment. Consult your dental professional to determine the most suitable treatment approach for your situation.
Preventing Gum Recession
While gum recession is a progressive condition, there are proactive steps you can take to slow or even halt its advancement. Here are some preventative measures to consider:
- Scheduling Regular Dental Check-ups: Routine visits to the dentist can help detect gum recession in its early stages and assist in maintaining overall oral health.
- Maintaining Good Oral Hygiene: Regular and proper brushing and flossing using a soft-bristled toothbrush can help prevent gum damage and recession.
- Eliminating Tobacco Use: Avoid all forms of tobacco, as it can adhere to teeth and contribute to gum recession and other dental issues.
- Adopting a Nutrient-Rich Diet: A diet abundant in vitamins, particularly Vitamin C, can bolster your defense against gum recession.
- Avoiding Oral Body Piercings: Lip or tongue piercings can irritate the gums and potentially lead to gum recession.
- Addressing Teeth Grinding and Clenching: If you have a habit of grinding or clenching your teeth, consider using a night guard, as recommended by your dentist, to shield your teeth and gums from excessive pressure.
- Seeking Orthodontic Treatment: Misaligned teeth can exacerbate gum recession. Orthodontic treatment can help correct alignment and reduce your risk.
By implementing these preventative measures, you can significantly lower your risk of developing gum recession. As the old adage goes, prevention is indeed better than cure.
Complications of Gum Recession
Gum recession, a common dental concern, can escalate into a myriad of complications if not addressed in a timely manner. Beyond the aesthetic impact on your smile, chronic gum recession can have far-reaching effects on your overall oral health. These effects can range from mild discomfort to severe conditions that require immediate attention. In the subsequent section, we delve into the potential repercussions of untreated gum recession on your oral health.
Impact on Oral Health
The effects of gum recession on oral health can be profound and wide-ranging if not promptly and effectively managed. Here’s a closer look at some of the possible complications:
- Tooth Sensitivity: As gum tissue recedes, it unveils more of the tooth’s root, potentially leading to heightened sensitivity to varying temperatures. A fluoride varnish applied by your dentist or hygienist may improve the symptoms of tooth sensitivity. Furthermore, you should consider prescription or over-the-counter toothpastes that are specifically formulated to help with tooth sensitivity.
- Increased Risk of Decay: The newly exposed tooth roots are more susceptible to bacterial invasion, raising the risk of cavities or decay. Fluoride treatment is highly recommended to patients with gingival recession to minimize the risk of decay.
- Tooth Loss: In extreme cases of gum recession, the loss of supporting tissue and bone can culminate in tooth loss.
- Aesthetic Implications: Gum recession can alter the appearance of your smile and impact your self-confidence. The exposed roots may modify the size and shape of your teeth, making them appear elongated.
- Periodontal Disease: Advanced stages of gum recession can evolve into periodontal disease, a severe condition characterized by inflammation, gum infection, and potential tooth loss.
It’s crucial to remember that early detection of gum recession and prompt treatment can help avert these complications. Regular dental check-ups and vigilance for any changes in your gums are key to ensuring your oral health remains in optimal condition.