Pediatric Dentistry
Pediatric dentistry is a cornerstone in laying the groundwork for lifelong dental health. This specialized field of dentistry zeroes in on the oral health of children, from their infancy through to their teenage years, extending care to those with unique healthcare requirements. The significance of pediatric dentistry is profound, as it not only facilitates early identification and management of dental problems but also cultivates good dental hygiene practices in children that they will carry forward into their adult lives.
Understanding Pediatric Dentistry
Often referred to as pedodontics, pediatric dentistry is a specialized branch of dental medicine dedicated to the oral health of children from birth through adolescence, inclusive of those with special healthcare needs. Pediatric dentists undertake additional years of training beyond dental school, equipping them to cater to the distinct dental needs of children. This extra training enables them to handle the behavioral aspects of children, their growth and development, and any special requirements they may have, ensuring their dental visits are comfortable and positive experiences.
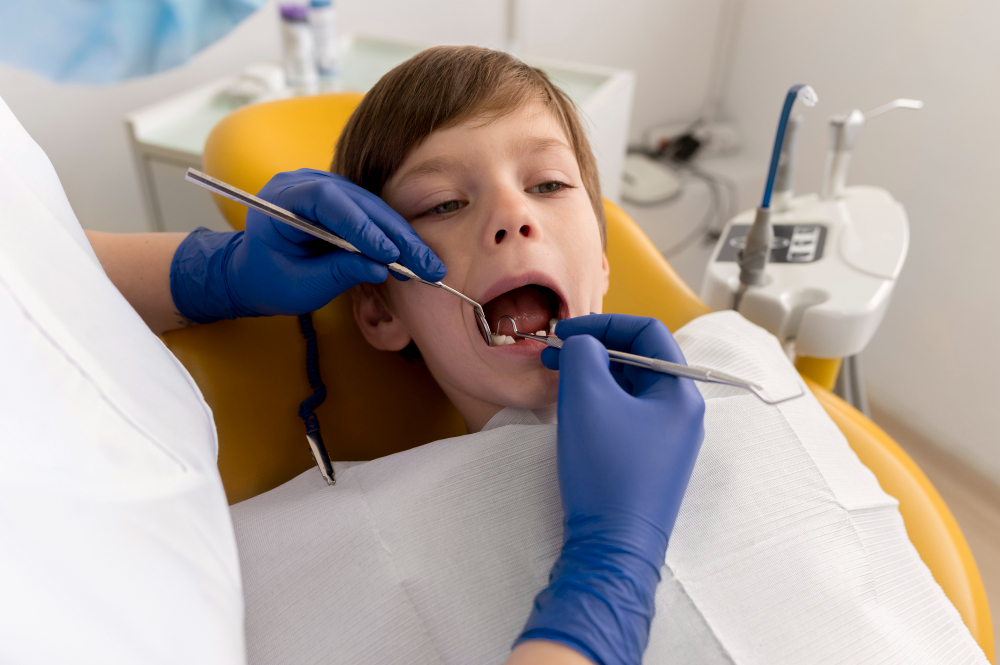
Pediatric dentists recognize that the dental needs of a child differ significantly from those of an adult. Primary teeth, also known as baby teeth, serve a crucial function in enabling children to chew and speak properly. Additionally, they reserve space for the permanent teeth developing beneath them and guide them into their correct positions. Therefore, preserving the health of these primary teeth until they naturally fall out is of paramount importance. Pediatric dentists offer comprehensive dental care that encompasses:
- Preventive measures
- Routine check-ups
- Guidance on proper brushing and flossing techniques
- Advice on diet and nutrition
- Habit counseling (such as pacifier use and thumb sucking)
- Treatment of dental injuries or conditions
The ultimate goal is to safeguard your child’s smile, both now and in the future.
Responsibilities of a Pediatric Dentist
Pediatric dentists, often referred to as pedodontists, shoulder a broad range of duties, all centered around delivering comprehensive oral care to children and adolescents.
Their primary obligation is to implement preventive oral health practices. This encompasses routine dental examinations, typically bi-annually, where they conduct meticulous teeth cleaning to eradicate plaque accumulation and avert cavities. They also administer dental sealants and topical fluoride treatments to young teeth, provide advice on nutrition and diet, and guide parents on the impact of oral habits such as pacifier use and thumb-sucking on dental health.
When dental issues arise, pediatric dentists are equipped to diagnose and address a myriad of conditions from tooth cavities to gum diseases, and dental injuries. They adeptly carry out procedures like fillings, extractions, and other necessary treatments, ensuring the child experiences minimal discomfort.
Pediatric dentists also play a crucial role in managing and treating dental health issues associated with underlying health conditions in children, such as diabetes, congenital heart defect, asthma, hay fever, and attention deficit/ hyperactivity disorder.
Monitoring children’s oral growth and development is another key responsibility. They are adept at identifying instances where orthodontic intervention may be needed in the future or where an underlying health condition could be impacting oral health.
Lastly, pediatric dentists are instrumental in counseling and education. They impart knowledge about good oral hygiene habits such as correct brushing and flossing techniques, offer guidance to parents on disease prevention, and stress the importance of a balanced diet in maintaining good oral health. This education is vital in fostering lifelong oral health habits in children, with the ultimate goal of arming both parents and children with the tools they need to maintain a healthy smile for life.
Common Dental Issues in Children
Just like adults, children can also fall prey to a range of dental issues. However, certain conditions are more prevalent during the formative years. Being aware of these common dental issues can enable parents and caregivers to act swiftly, reducing the discomfort for their child and effectively managing any potential impact on their overall oral health.
Tooth decay, or dental cavities, tops the list of common dental issues in children. This condition arises when harmful bacteria in the mouth use sugars from food and drinks to create acids that wear away the tooth enamel, resulting in cavities.
Gum disease, while not as widespread among children as adults, can still occur, especially in adolescents. Dental plaque, a bacterial film on the teeth, is the main culprit behind gum disease, causing gum inflammation that can lead to pain, discomfort, and even tooth loss if not addressed.
It’s crucial to remember that these dental problems can be largely prevented through regular dental cleanings, a balanced diet, and a consistent oral hygiene routine. Pediatric dentists are key in diagnosing and treating these issues early, underlining the importance of routine dental check-ups.

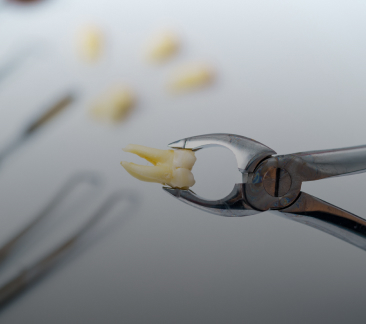
Tooth Decay and Cavities
Tooth decay, leading to cavities, is a prevalent dental concern in children. Cavities are essentially tiny holes that develop in the teeth due to prolonged decay. If neglected, they can trigger severe toothaches, infections, and even tooth loss.
The decay process initiates with dental plaque, a sticky film teeming with bacteria that accumulates on the teeth. These bacteria feast on sugars from our diet, producing acids that gradually erode the tooth’s hard outer layer, the enamel. As the enamel weakens, cavities begin to appear.
Cavity symptoms can vary, often depending on the decay’s extent and the affected tooth’s position. In the early stages, decay may not show any signs. However, as the cavity deepens, symptoms may emerge such as toothache, sensitivity to temperature and sweetness, visible holes in the teeth, and in some cases, tooth discoloration.
Pediatric dentists employ a combination of a clinical examination and dental X-rays to diagnose cavities. X-rays can reveal cavities forming in areas not visible to the naked eye, such as between teeth and under the gum line.
Early detection and intervention are crucial to halt the progression of tooth decay and associated complications. Depending on the decay’s severity, pediatric dentists offer a range of treatments, including fillings, crowns, pulp therapies, and even extractions.
Prevention is the most effective strategy against tooth decay and cavities. Regular dental check-ups, good oral hygiene, and a balanced, low-sugar diet are key preventative measures.
Gum Diseases
Gum disease, or periodontal disease, is an inflammation and infection of the tissues that support and surround the teeth. While less common in children, the likelihood of gum diseases increases with age, particularly during adolescence.
Gum diseases are typically categorized into two stages. The initial stage, gingivitis, is marked by swollen, red gums that bleed easily during brushing or flossing. This is usually caused by plaque build-up along and under the gum line, which irritates the gum tissue. If left untreated, gingivitis can progress to periodontitis.
Periodontitis, the more severe stage, can cause the gums to recede from the teeth, creating pockets that can harbor infection. In extreme cases, it can even affect the bone supporting the teeth, leading to loose teeth or tooth loss.
Symptoms of gum diseases can include sensitive, tender, or red gums, bleeding while brushing or flossing, receding gums, persistent bad breath, or a change in the child’s bite.
Diagnosis of gum diseases involves assessing gum inflammation, plaque, and tartar build-up, checking for easy bleeding, and measuring the depth of gum pockets if present. Dental X-rays may also be used to detect any bone loss.
Treatment options for gum diseases depend on the severity and can range from professional dental cleaning to remove plaque and tartar, a regimen of proper brushing and flossing, and in severe cases, medication or surgery may be required.
Prevention is key in managing gum diseases. Regular dental check-ups for early detection and intervention, maintaining good oral hygiene, and a balanced diet free of excessive sugary and acidic foods are crucial preventative measures.
Pediatric Dental Procedures
Pediatric dentistry encompasses a wide array of procedures, each tailored to safeguard and enhance a child’s dental health. These procedures can be broadly categorized into preventive and treatment measures.
Preventive dental care aims to fortify a child’s teeth against potential future issues. This category includes regular dental examinations, professional teeth cleaning, and the application of dental sealants. These procedures are designed to nip potential dental problems in the bud, ensuring the child’s oral health remains in top-notch condition.
Conversely, treatment measures are designed to tackle existing dental issues. These procedures, which include dental fillings for tooth decay and cavities, extractions for severely damaged teeth, and other treatments for more complex dental diseases, are crucial in restoring a child’s oral health.
It is important to discuss the role of sedation in pediatric dentistry. Due to fear, anxiety and other behavioral issues, most children require some form of sedation to receive dental care. The level of sedation may include nitrous oxide, oral sedatives, IV sedation and even general anesthesia. Discuss with your pediatric dentist and anesthesiologist which sedation option is the most appropriate for your child.
By understanding the range of procedures available in pediatric dentistry, parents can gain a comprehensive overview of how to prevent and treat dental ailments, thereby ensuring their child’s oral health is effectively managed. The following sections delve deeper into preventive and treatment measures.
Preventive Measures: Check-ups and Cleaning
The cornerstone of pediatric dentistry lies in its emphasis on preventive measures, which include regular dental check-ups and professional teeth cleaning. These routine visits are instrumental in early detection of potential dental issues, thereby reducing the risk of further complications.
During a check-up, the pediatric dentist conducts a meticulous examination of the child’s oral cavity, including the teeth and gums. This allows for the identification of any signs of cavities, gum diseases, or other dental issues. It also provides an opportunity to assess the child’s dental development. Tools commonly used during these examinations include dental mirrors, probes, and occasionally, X-rays for a more detailed view.
Professional cleaning is also performed during these visits. This procedure involves the removal of dental plaque and tartar that regular brushing and flossing at home may miss. The process includes scaling, which involves scraping off tartar from above and below the gum line, and polishing to remove any remaining stains and plaque, followed by flossing.
Pediatric dentists also offer additional preventive treatments such as fluoride treatments and dental sealants. Fluoride helps to fortify tooth enamel, reducing the likelihood of decay, while sealants act as a protective shield against cavity-causing bacteria, typically applied to the chewing surfaces of the back teeth.
The frequency of these dental check-ups can vary based on the child’s individual needs. However, it is generally recommended for children to visit the dentist every six months for preventive care. Parents are encouraged to consult with their child’s dentist to establish an appropriate check-up schedule.
Treatment Measures: Fillings and Extractions
In instances where preventive strategies fall short, pediatric dentists resort to treatment measures such as fillings and extractions to address cavities or tooth damage in children.
Fillings, a standard procedure in pediatric dentistry, are employed to treat cavities. The process involves the removal of the decayed tooth portion, followed by thorough cleaning of the cavity. Subsequently, a filling material – typically composite resin, silver amalgam, or porcelain – is used to fill the cavity. This step is crucial as it prevents bacteria from invading the cavity, thereby safeguarding the tooth from further decay. Most often, a single visit suffices to complete this procedure, depending on the cavity’s severity.
Extractions, on the other hand, involve the removal of teeth and are performed under various circumstances. These include severe tooth decay unresponsive to fillings or crowns, an overcrowded mouth necessitating tooth removal for orthodontic treatment, or irreparable tooth damage post-accident. Similar to fillings, extractions are typically completed within a single visit.
Post-procedure, the pediatric dentist will offer advice on ensuring proper healing, infection prevention, and discomfort management. This may encompass suggestions for over-the-counter pain relief, dietary restrictions, and maintaining oral hygiene during the healing phase.
It’s crucial to remember that while fillings and extractions are routine procedures, they are generally considered a last resort. The focus is always on preventive therapies to halt the progression of dental diseases before they necessitate these types of treatments.
Promoting Dental Health in Children
The responsibility of safeguarding children’s dental health extends beyond the pediatric dentist’s office. It also hinges on fostering good oral hygiene habits at home and making nutritious dietary choices. This collaborative approach can significantly contribute to preventing dental diseases and establishing a robust foundation for lifelong dental health.
Promotion of dental health involves teaching children the correct brushing and flossing techniques, helping them understand their importance, and motivating them to incorporate these practices into their daily routine. Additionally, diet significantly impacts oral health. A balanced and nutritious diet can lead to stronger teeth and healthier gums. Conversely, excessive consumption of sugary foods and beverages can expedite tooth decay.
The subsequent sections delve deeper into promoting oral hygiene practices and dietary habits for optimal dental health in children. When combined with regular dental check-ups, these efforts form a holistic strategy for preventive dental care.
Proper Brushing and Flossing Techniques
The cornerstone of pediatric dental health lies in mastering the art of brushing and flossing. From the moment the first tooth sprouts, it’s crucial to establish a regular cleaning routine. This can start with a soft cloth or baby toothbrush to gently clean the tooth and gums.
As your child matures, they should learn to maneuver the toothbrush themselves, covering all surfaces of each tooth with gentle circular strokes. This twice-daily routine should span two minutes each time, ideally in the morning and before bedtime.
Flossing becomes necessary once two teeth grow close enough to touch. Children should be guided to move the floss up and down against each tooth, reaching under the gum line where plaque tends to accumulate.
The importance of tongue cleaning should not be overlooked, as it can help to minimize bacteria and freshen breath. Until around the age of 7 or 8, parents should oversee these dental hygiene practices to ensure their effectiveness.
Toothbrushes should be replaced every three to four months, or when the bristles start to fray, to maintain their efficacy in plaque removal. A small, soft-bristled toothbrush is usually the most suitable for children.
Fluoridated toothpaste is advisable, but in minimal amounts for young children to prevent fluorosis, a condition caused by excessive fluoride that can discolor the teeth. A smear the size of a grain of rice is adequate for toddlers, increasing to a pea-sized amount from the age of three. Adhering to these steps can significantly enhance the effectiveness of your child’s brushing and flossing routine, providing a solid defense against common pediatric dental issues.
Diet and Oral Health
The impact of diet on dental health is profound. The type and frequency of foods children consume can have a significant bearing on their dental health.
Frequent consumption of sugary foods and drinks can instigate tooth decay. The sugar interacts with oral bacteria to produce acids that erode tooth enamel, leading to cavities. Consequently, it’s advisable to limit the intake of sweets, cookies, sugary drinks, and even fruit juices.
Carbohydrate-rich foods like bread and pasta can also contribute to tooth decay, as they break down into simple sugars in the mouth. Therefore, it’s not just sweets that pose a threat to dental health, but the frequency of carbohydrate consumption should also be monitored.
In contrast, foods that bolster oral health should be encouraged. Calcium-rich foods like milk, cheese, and yogurt are vital for reinforcing tooth enamel. Foods high in phosphorus, such as meat, eggs, and fish, can also help maintain enamel strength. Crunchy fruits and vegetables, like apples, carrots, and celery, serve a dual purpose by providing nutrition and naturally cleaning the teeth while stimulating saliva production to neutralize harmful acids.
Water, especially fluoridated water, plays a crucial role in rinsing away food particles and keeping the mouth hydrated, thereby reducing the risk of tooth decay.
Promoting healthy eating patterns, such as regular, balanced meals instead of frequent snacking, can help prevent a constant supply of sugar that fuels acid production. By instilling these balanced dietary habits early on, coupled with proper oral hygiene practices, you can significantly contribute to your child’s oral and overall health.
Parental Role in Pediatric Dentistry
The success of pediatric dentistry is significantly amplified when parents take an active role in their child’s dental health. Parents are instrumental in shaping positive dental experiences, nurturing good oral hygiene habits, and ensuring regular dental visits.
Parents are the initial educators in oral care, teaching their children the correct way to brush and floss their teeth. They are responsible for providing a balanced diet that promotes healthy gums and teeth and setting an example through their own oral hygiene habits. Moreover, their attitude towards dental visits can greatly influence a child’s perception, thereby reducing potential dental anxiety.
The involvement of parents is undeniably vital and remains the primary influence on a child’s dental health until they reach an age where they can independently manage their oral care. The subsequent sections will delve into the specifics of the roles parents play in fostering positive dental experiences and nurturing good oral hygiene habits.
Creating Positive Dental Experiences
Parents significantly influence their children’s outlook, and hence, have a crucial role in molding positive dental experiences. These initial experiences can profoundly impact a child’s attitude towards dental health as they mature.
Introducing regular dental visits at an early age can familiarize a child with the dentist’s office, making them more comfortable. The American Academy of Pediatric Dentistry advises scheduling the first dental visit when the first tooth appears or by the child’s first birthday at the latest.
Portray dental visits as a positive experience, avoiding any association with pain or fear. Use straightforward, reassuring language to explain what will occur during a check-up. Strive to keep the child relaxed and at ease before and during the visit.
Encourage the child to bring a beloved toy or comfort item to the dentist, and acknowledge good behavior with praise or a non-sugary reward after the visit.
Parents can also engage in role-playing games, pretending to be the ‘tooth doctor,’ examining their child’s teeth. This approach not only familiarizes children with a dental check-up but also makes it enjoyable.
Bear in mind that children often emulate their parents, so demonstrating a positive attitude towards dental hygiene, check-ups, and dentists can significantly influence a child’s perception.
Maintaining a regular visit schedule and a consistent relationship with the child’s dentist helps establish trust and makes the child more comfortable during actual procedures.
Cultivating positive dental experiences early on will not only ensure your child’s teeth are healthy but also lay the groundwork for good dental practices in their adulthood.
Instilling Good Oral Hygiene Habits
The role of parents in pediatric dentistry extends beyond scheduling regular check-ups; it includes fostering a strong foundation of oral hygiene habits in children.
Firstly, it’s essential to communicate the significance of maintaining oral health to children. Break down the potential repercussions of neglecting oral hygiene, like cavities and gum disease, into simple, child-friendly terms.
The next step is to create a steady oral care routine at home. This should involve brushing their teeth twice a day for two minutes each time and flossing daily. Regularity in these practices helps children perceive them as normal daily activities, making it more likely they’ll continue these habits into adulthood.
To make oral hygiene enjoyable for children, consider incorporating fun elements. A toothbrush featuring their beloved cartoon character or a toothpaste with a flavor they love can make brushing an exciting task. Additionally, children’s books and songs about dental care can add an entertaining twist to the routine.
Remember, children often emulate what they see. Regularly demonstrating good oral hygiene habits can encourage them to follow suit. Turning brushing time into a family activity can also make it more appealing for the child.
Regular dental check-ups should be a part of this routine. These visits not only provide an opportunity for the pediatric dentist to assess the child’s oral health but also emphasize the importance of dental care.
Promoting a balanced diet and reducing the intake of sugary snacks and drinks is another crucial step. Help children understand the link between their food choices and dental health.
The oral hygiene habits that children adopt at a young age often persist into adulthood, making early education and practice a worthwhile investment in their long-term dental health.
Schedule Today!
We look forward to meeting you. Call us or request an appointment online to set up your first visit. We’ll be in touch soon.

