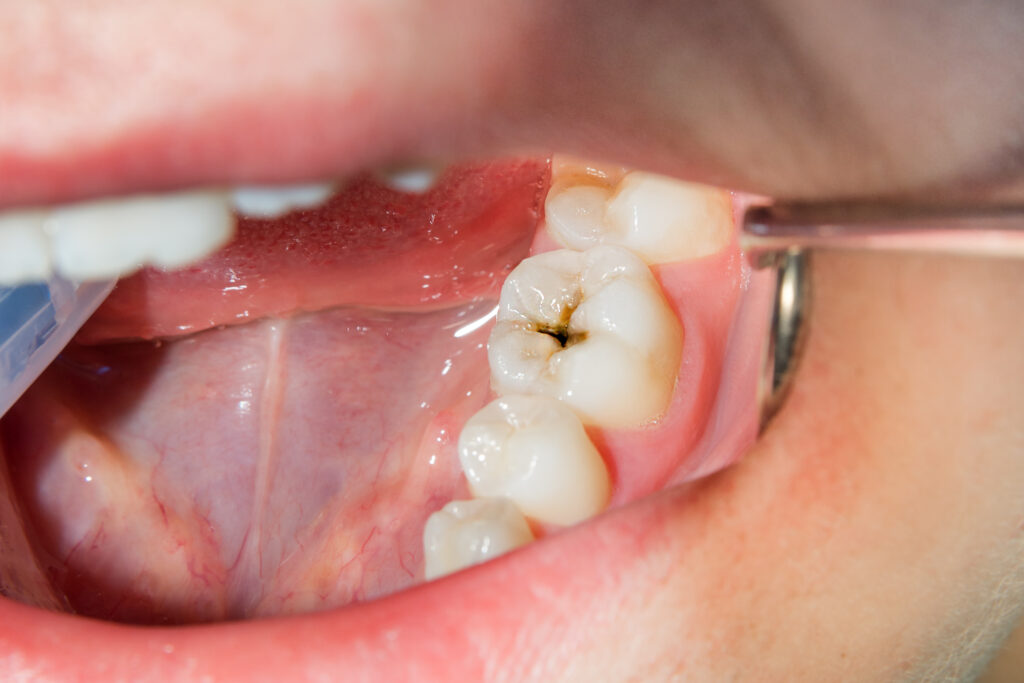
When was the last time you had your teeth checked?
You might think regular dental check-ups are unnecessary. After all, your teeth feel fine. However, tooth decay is a slow process that might occur for years before you have symptoms, subtly weakening your teeth and eventually causing severe damage.
Cavities form when tooth decay progresses unchecked. Acids from food residue and oral bacteria erode the enamel, forming tiny holes which expand over time and compromise the tooth’s structure.
While fillings can halt a cavity in its early stages, such procedures aren’t sufficient if the cavity has gone untreated for too long.
So at what point can a cavity not be fixed? Let’s find the answer to this concerning question as we look at what happens when you leave tooth decay untreated.
How Long Can Tooth Decay Be Left Untreated?
Various factors determine how long a cavity can go without treatment. For instance, good oral hygiene, such as brushing and flossing, may slow the progression of tooth cavities.
Additionally, small and shallow cavities might not cause immediate pain or infection. The enamel is harder than steel. Cavities might take up to five years before reaching the dentin layer beneath. However, an unhealthy diet can accelerate the decay process. Sugary foods and drinks weaken the enamel and create a breeding ground for harmful oral bacteria.
Age also determines how long you can go without treating a cavity. For example, cavities progress faster in children since their teeth aren’t fully developed. On the other hand, gum recession in older adults makes them vulnerable to bacterial infections and deep cavities.
Finally, genetics and health also determine how long it takes a cavity to develop. For example, medical conditions such as diabetes weaken the immune system making you vulnerable to oral infections and rapid cavity formation.
So, how long can you go with a cavity? Honestly, there isn’t an established timeline for cavity progression since the factors mentioned above vary from individual to individual.
What Happens if You Have a Cavity for Too Long?
To answer the question, it’s important first to understand the stages of tooth decay.
White Spots
Catching tooth decay in its early stages is almost impossible without regular dental check-ups. In particular, the subtle white spots that appear as oral bacteria attack your tooth might seem harmless to the untrained eye. Meanwhile, the bacteria slowly corrode protective minerals from the enamel, making it more porous and susceptible to cavities.
Enamel Decay
Cavities start forming at this stage and can progress rapidly if left unchecked. Oral bacteria will wreak havoc by weakening the enamel and making your tooth more vulnerable to decay. Remember that various factors, such as oral hygiene and diet, will determine how fast the cavities form.
Dentin Decay
As the decay progresses, it will reach the dentin layer beneath the enamel. This layer lies above the innermost part of the tooth. The cavity will grow larger and progress faster since the dentin is softer than the enamel. You are most likely to start feeling the effects of tooth decay at this stage. Examples include sensitivity to cold or hot foods and discomfort when chewing.
Pulp Infection
This is the critical stage for tooth decay. The pulp is the innermost part of the tooth containing its nerves and blood vessels. If the infection continues to run rampant, you’ll experience severe pain, swollen gums, and bad breath. In most cases, fillings and fluoride treatments are insufficient at this stage.
Abscess Formation
This is the final stage of tooth decay. It occurs if a cavity is left untreated for too long. The infection festers and spreads beyond the tooth, affecting the surrounding teeth and gum tissue. A pocket of pus or abscess will form, causing severe complications such as pain, fever, and swelling.
The Impacts of Neglecting Dental Decay Treatment
It’s easy to see why dental check-ups are recommended at least once every six months when considering the adverse consequences of rampant tooth decay.
These consequences include:
Tooth Pain and Sensitivity
The acids produced by oral bacteria demineralize your teeth and erode the enamel. This causes your teeth to become vulnerable and extremely sensitive to temperature changes. As a result, you might experience pain when eating hot and cold foods.
Tooth Infection
Cavities provide an ideal breeding ground for oral bacteria. If left untreated, the bacteria will thrive and infect the inner layers of the tooth that contain the blood vessels and nerves. Such an infection can lead to severe dental complications such as swelling, abscess formation, and severe pain.
Bad Breath
Oral bacteria multiply and build up if the tooth cavity is left untreated. The waste the bacteria produce as they break down the tooth can cause halitosis or bad breath.
Tooth Loss
Tooth loss is one of the worst outcomes of tooth decay. An untreated cavity will weaken your tooth over time, making it impossible to save. In such cases, tooth extraction is the only viable option. As you can imagine, losing a tooth can lead to difficulty speaking and eating and negatively impact your confidence.
At What Point Can a Cavity Not Be Fixed?
There’s no doubt that cavity fillings are effective at halting tooth decay. However, fillings only work when tooth decay hasn’t compromised the tooth’s structure. Extensive procedures may be the only option once the infection reaches the pulp and significantly weakens the tooth.
While tooth extraction is an option, it’s usually the last resort. Your dentist might suggest a root canal procedure to save the tooth. This procedure involves removing the infected dental pulp, cleaning the inside of the tooth, and shaping the root canals. The canals are then sealed with gutta-percha to prevent infection.
Remember that tooth extraction and root canal procedures are only necessary once tooth decay reaches its final stages. Regular dental check-ups will help detect and treat cavities before they can severely damage the tooth.
Preventing Dental Caries and Cavity Formation
Tooth decay and cavities can be detrimental to your quality of life. The good news is that there are several simple but effective strategies for preventing tooth decay and cavity formation.
They include:
- Brush your teeth regularly: Brushing at least twice a day significantly reduces the risk of cavity formation. Not only does brushing remove plaque, but it can also help preserve your gums, preventing infection and gum disease.
- Floss daily: Flossing allows you to clean the gum line and hard-to-reach areas between your teeth. Flossing at least once daily will reduce bacteria, plaque, and food residue buildup.
- Watch your diet: Sugary and acidic foods and drinks act as catalysts for tooth decay. Such foods demineralize your teeth; and oral bacteria thrive on sugary food residue. After consuming such foods, you should brush your teeth or rinse your mouth with water.
- Avoid smoking: Cigarette smoke increases the risk of tooth decay, cavity formation, and gum disease. Cigarette smoke raises acidity levels in the mouth by reducing saliva formation. It also weakens the gums making it easier for bacteria to infiltrate your teeth, causing cavities and infection.
- Drink plenty of water: Water washes away food residue and neutralizes acidity in the mouth. It also increases saliva production, which helps lower acidity and reduces plaque buildup.
- Chewing sugar-free gum: Chewing sugar-free gum after meals is an effective way to clean your teeth. Apart from stimulating saliva production, chewing gum helps clean out teeth crevices.
- Apply dental sealants: You should consider dental sealants if the chewing surfaces of your molars are weak. Dental sealants act as a protective coating for your enamel, keeping them safe from oral bacteria and corrosive elements.
While the tips above are effective at preventing cavity formation and tooth decay, they work best when coupled with regular oral check-ups. Dental check-ups allow early detection of cavities, gum disease, and tooth decay. Moreover, your dentist can recommend preventive measures such as dental sealants, which can prevent the formation of cavities.
Finally, plaque and tartar might build up despite practicing good oral hygiene. In this case, your dental professional will perform a professional cleaning to rid your teeth of this buildup and reduce the risk of tooth decay.
To summarize, leaving tooth decay untreated for too long is a recipe for disaster. While the short-term effects of tooth decay are bad enough, allowing a cavity to go for too long can have severe consequences, such as severe pain, abscess formation, fever, and tooth loss.
With this in mind, you can’t afford to overlook your oral health. Make a point of going for dental check-ups at least twice a year and prevent tooth decay before it can develop into a severe problem.